01 Jan
IDO1/キヌレニン/AhR軸を介したマクロファージにおけるNMNの抗炎症機能

1. はじめに
Nイコチンアミドモノヌクレオチド(NMN)supplementation has been suggested to hamper the inflammatory responses via restoring NAD+ level and downregulating the expression of Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Strikingly, both Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), two key enzymes for kynurenine production, can mediate the anti-inflammatory function of NMN(エヌエヌ) in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
2.NMN補給の存在下での緩和された炎症反応
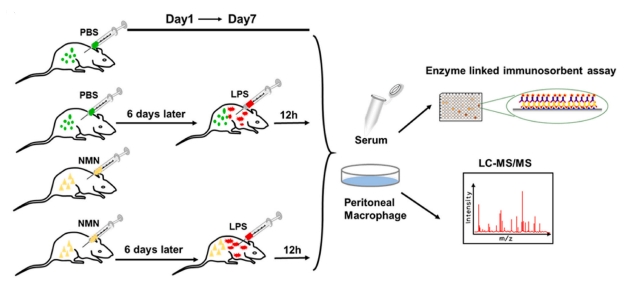
For deciphering the impact of NMN in vivo, mice are subjected to daily intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of NMN (500 mg/kg) for consecutive 6 days, followed by i.p. injection of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) (5 mg/kg) or alum (700 μg) on day 7. It is discovered that NMN supplementation suppresses LPS- or alum-induced inflammation in mice, as manifested by the downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and IL-1β) and proinflammatory enzyme (COX-2).


3. NMNを介したマクロファージの炎症反応抑制におけるAhRの必要性
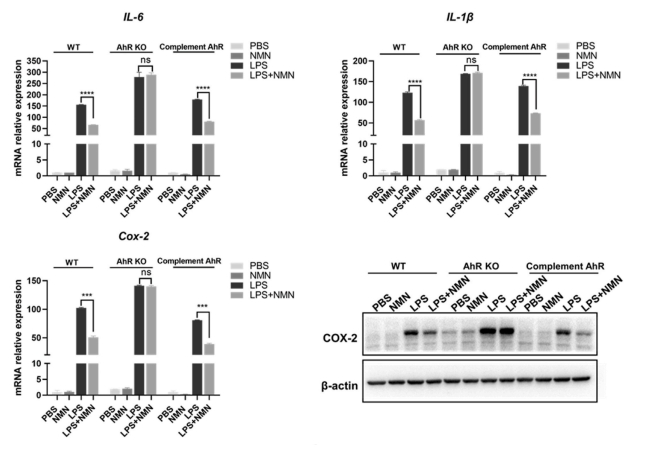
AhR, a ligand-activated transcription factor, can mediate the anti-inflammatory function of NMN upon LPS treatment in RAW264.7 cells. Specifically, NMN reduces the expression of COX-2 in cells in bearing AHR. On the contrary. AhR inhibitor (CH223191) deprives the downregulation of IL-6, IL-1β and COX-2 caused by NMN treatment. Likewise, NMN treatment fails to reduce the expression levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and COX-2 in AhR knockout cells.


4. NMNの抗炎症機能におけるIDO1/キヌレニン/AhR軸の重要性
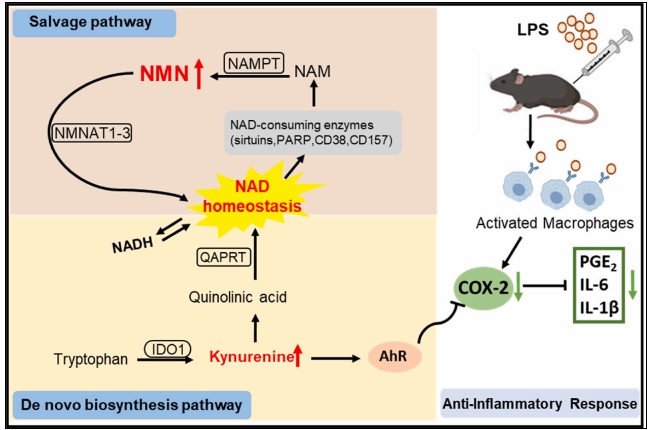
IDO1 is the rate-limiting enzyme in tryptophan catabolism to produce kynurenine, a metabolic intermediate in NAD+ de novo synthesis pathway. Kynurenine can promote the translocation of AhR from the cytoplasm to nucleus, thereby exerting an anti-inflammatory effect. NMN inhibits LPS-induced inflammation in a IDO1-kynurenine dependent manner in macrophages.

5. おわりに
NMN supplementation mitigates COX-2-associated inflammatory responses by activating lDO-kynurenine-AhR pathway, providing new insights into NAD* regulation in macrophage activation.
参考
Liu J, Hou W, Zong Z, et al. Supplementation of nicotinamide mononucleotide diminishes COX-2 associated inflammatory responses in macrophages by activating kynurenine/AhR signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. Published online February 8, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.01.046
ボンタックNMN
ボンタック is the pioneer of NMN(エヌエヌ)industry and the first manufacturer to launch NMN(エヌエヌ) mass production, with the first whole-enzyme catalysis technology around the world. At present, ボンタック has become the leading enterprise in niche areas of coenzyme products.

Notably, BONTAC is the NMN raw material supplier of famous David Sinclair team at the Harvard University, who uses the raw materials of BONTAC in a paper titled “Impairment of an Endothelial NAD+-H2S Signaling Network Is a Reversible Cause of Vascular Aging”. Our services and products have been highly recognized by global partners. Furthermore, BONTAC has the first national and the only provincial independent coenzyme engineering technology research center in Guangdong, China. The coenzyme products of BOMNTAC are widely used in fields such as nutritional health, biomedicine, medical beauty, daily chemicals and green agriculture.

Notably, BONTAC is the NMN raw material supplier of famous David Sinclair team at the Harvard University, who uses the raw materials of BONTAC in a paper titled “Impairment of an Endothelial NAD+-H2S Signaling Network Is a Reversible Cause of Vascular Aging”. Our services and products have been highly recognized by global partners. Furthermore, BONTAC has the first national and the only provincial independent coenzyme engineering technology research center in Guangdong, China. The coenzyme products of BOMNTAC are widely used in fields such as nutritional health, biomedicine, medical beauty, daily chemicals and green agriculture.
免責事項
This article is based on the reference in the academic journal. The relevant information is provide for sharing and learning purposes only, and does not represent any medical advice purposes. If there is any infringement, please contact the author for deletion. The views expressed in this article do not represent the position of BONTAC.
Under no circumstances will BONTAC be held responsible or liable in any way for any claims, damages, losses, expenses, costs or liabilities whatsoever (including, without limitation, any direct or indirect damages for loss of profits, business interruption or loss of information) resulting or arising directly or indirectly from your reliance on the information and material on this website.
Under no circumstances will BONTAC be held responsible or liable in any way for any claims, damages, losses, expenses, costs or liabilities whatsoever (including, without limitation, any direct or indirect damages for loss of profits, business interruption or loss of information) resulting or arising directly or indirectly from your reliance on the information and material on this website.
